+86-18343147735
+86-18343147735




A urine test, often referred to as a urinalysis, is a crucial diagnostic tool used in the medical field to evaluate a person's health status. By analyzing the composition and characteristics of urine, healthcare providers can gain valuable insights into various bodily functions and identify potential health issues. This non-invasive and relatively straightforward procedure offers a wealth of information, making it an essential part of routine health assessments and disease diagnostics.
The process of conducting a urine test involves collecting a sample of urine and subjecting it to a variety of analyses, including chemical, physical, and microscopic examinations. Each of these components contributes to a comprehensive understanding of an individual's health, allowing for the detection of conditions such as infections, kidney disease, and metabolic disorders. As a result, the urine test plays a foundational role in preventative health care and the early detection of medical conditions, thereby aiding in timely intervention and management.
In summary, a urine test is not just a simple evaluation of waste products but a vital component of overall health diagnostics. Its ability to reflect various physiological changes underscores its significance in modern medicine, serving both as a screening tool and a means of monitoring ongoing health issues. Understanding the intricacies of urine testing can empower individuals to take charge of their health and engage meaningfully with their healthcare providers.

A urine test, also known as urinalysis, is a diagnostic tool used to assess various health aspects by examining the chemical and physical properties of urine. This non-invasive test can provide valuable insights into a person's metabolic state, kidney function, and potential infections. According to the National Institute of Health, urine tests can detect signs of conditions such as diabetes, kidney disease, and urinary tract infections, making it a critical component in routine health screenings.
In a typical urine test, a sample is collected and analyzed for several key indicators, including pH level, protein, glucose, ketones, and the presence of red or white blood cells. These parameters can reveal underlying health issues. For instance, the presence of glucose may hint at diabetes, while an elevated amount of protein may indicate kidney problems. The American Urological Association notes that approximately 30% of chronic kidney disease cases can be identified through irregularities in urinalysis, highlighting its importance in preventive healthcare.
Tips: To improve the accuracy of urine tests, it’s essential to provide a clean sample. Patients should follow any pre-test instructions provided by their healthcare provider, which may involve fasting or avoiding certain foods and medications. Staying well-hydrated before the test can also ensure a sufficient urine sample, enhancing the test's reliability.
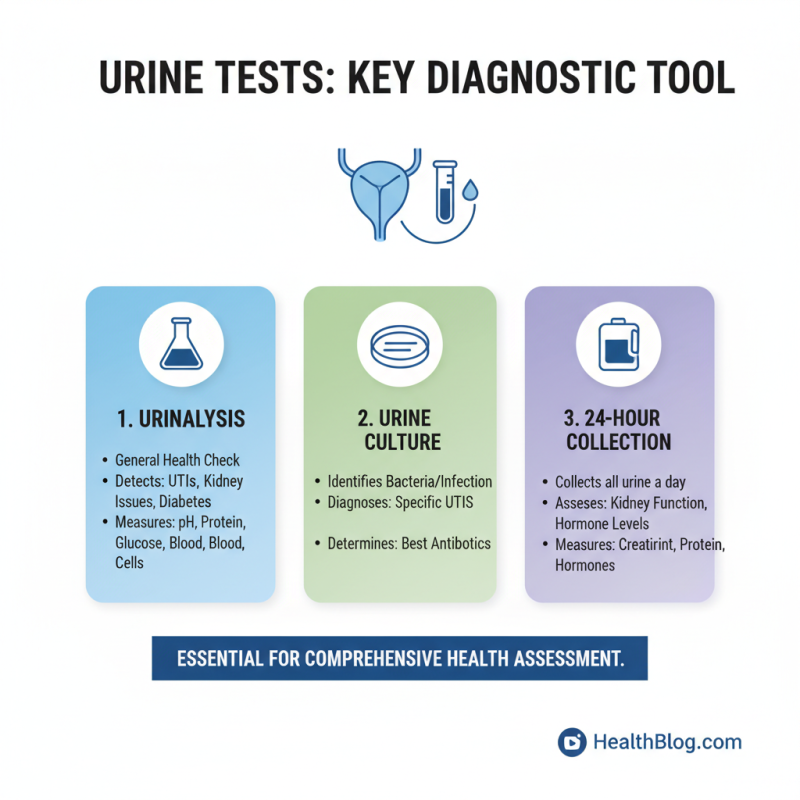
Urine tests are an essential tool in health diagnosis, utilized for a variety of medical assessments. There are several types of urine tests, each tailored to detect specific health issues. The most common types include urinalysis, urine culture, and 24-hour urine collection.
Urinalysis is a comprehensive test that evaluates various components of urine, such as pH, specific gravity, protein, glucose, and the presence of red or white blood cells. According to the American Urological Association, urinalysis is pivotal in diagnosing conditions like urinary tract infections (UTIs), kidney disorders, and diabetes. A study published in the Clinical Biochemistry Reviews emphasizes that up to 80% of all medical conditions can be identified through effective urinalysis techniques.
Urine culture, on the other hand, is specifically aimed at identifying bacterial infections in the urinary tract. It can isolate pathogens and determine antibiotic susceptibility, providing healthcare providers with critical information to tailor treatments. The Infectious Diseases Society of America notes that timely and accurate urine cultures can significantly improve patient outcomes, especially in populations predisposed to recurrent UTIs.
Lastly, the 24-hour urine collection test measures various substances in urine over a full day, offering a comprehensive view of kidney function and metabolic conditions. This method is particularly effective in assessing disorders such as kidney stones and pheochromocytoma. According to a report from the National Kidney Foundation, these tests are crucial for understanding the underlying causes of kidney issues, thus allowing for better patient management and therapeutic strategies.
A urine test is a common diagnostic tool used by healthcare professionals to assess an individual's overall health and detect various medical conditions. The process of conducting a urine test typically begins with the collection of a urine sample. Patients may be asked to provide a midstream urine sample, which involves the initial part of urination being discarded to avoid contamination. This method helps ensure accuracy, as it minimizes the presence of bacteria or impurities from the urethra.
Once the sample is collected, it is sent to a laboratory for analysis. In the lab, technicians perform various tests, including visual inspection, chemical analysis, and microscopic examination. According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), urine tests can aid in diagnosing conditions such as urinary tract infections, diabetes, and kidney disease. These tests can reveal vital indicators like protein levels, glucose concentration, and the presence of red or white blood cells. Research indicates that approximately 80% of all medical diagnoses are based on laboratory test results, making urine tests a critical component of successful health assessments.
This chart illustrates the common components measured in a standard urine test, representing their average concentration levels in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). The data reflects a typical healthy range for adults.
Interpreting urine test results is a crucial aspect of diagnosing various health conditions.
Urinalysis, which includes physical, chemical, and microscopic evaluations of urine, helps healthcare professionals detect abnormalities.
For instance, the presence of glucose in urine may indicate diabetes, while elevated levels of protein can signal kidney issues.
According to the National Kidney Foundation, even minor changes in urine composition can provide valuable insights into a patient's health,
making urine tests a commonly utilized diagnostic tool.
Additionally, urine color and clarity can provide immediate visual cues about hydration status and potential health concerns.
For instance, dark yellow urine typically indicates dehydration, while cloudy urine may suggest an infection.
A report by the American Urological Association highlights that urine tests are not only useful for diagnosing urinary tract infections but can also assist in screening for systemic conditions like metabolic disorders.
By analyzing the results accurately, healthcare providers can formulate a more effective treatment plan tailored to the patient's unique health needs.
Urine tests, or urinalysis, serve as a vital tool in the medical field for diagnosing various health conditions. These tests evaluate the chemical and physical properties of urine, providing insights into the functioning of the kidneys and urinary tract. According to the National Institutes of Health, urinalysis can detect abnormalities that indicate a range of health issues, with sensitivity rates for certain conditions, such as diabetes and urinary tract infections (UTIs), exceeding 90%.
Common health conditions that can be identified through urine tests include diabetes mellitus, where the presence of glucose and ketones in the urine signals the body's inability to regulate blood sugar effectively. Further, urinary tract infections are frequently detected through the identification of nitrites or leukocytes in urine, indicating an infection. Additionally, renal disorders such as glomerulonephritis can be suspected based on the presence of protein or blood in the urine. According to the American Urological Association, approximately 20% of patients with unexplained kidney issues show positive outcomes for significant markers during urinalysis.
The ability to detect such conditions through urine tests underlines their significance in routine health check-ups. A report by the World Health Organization highlights that early detection through simple tests can lead to improved health outcomes, with timely medical intervention reducing complications associated with chronic diseases. Overall, urine tests play an essential role in preventative healthcare strategies, allowing for early diagnosis and management of various health conditions.