+86-18343147735
+86-18343147735




The Hemoglobin Blood Test is a vital diagnostic tool that provides essential insights into an individual’s overall health. Hemoglobin, the protein in red blood cells responsible for transporting oxygen throughout the body, plays a crucial role in maintaining various bodily functions. A well-functioning hemoglobin level is not just indicative of a healthy oxygen supply; it also reflects the body's ability to produce red blood cells efficiently.
This test is particularly important as it helps identify potential health issues such as anemia, which can result from various factors including nutritional deficiencies, chronic diseases, or bone marrow disorders. Early detection of abnormalities in hemoglobin levels allows for timely intervention and management of underlying conditions, promoting better health outcomes. Understanding the significance of the Hemoglobin Blood Test is essential for both healthcare providers and patients, as it can serve as a critical indicator of one’s general well-being and help guide further medical evaluations or treatments.
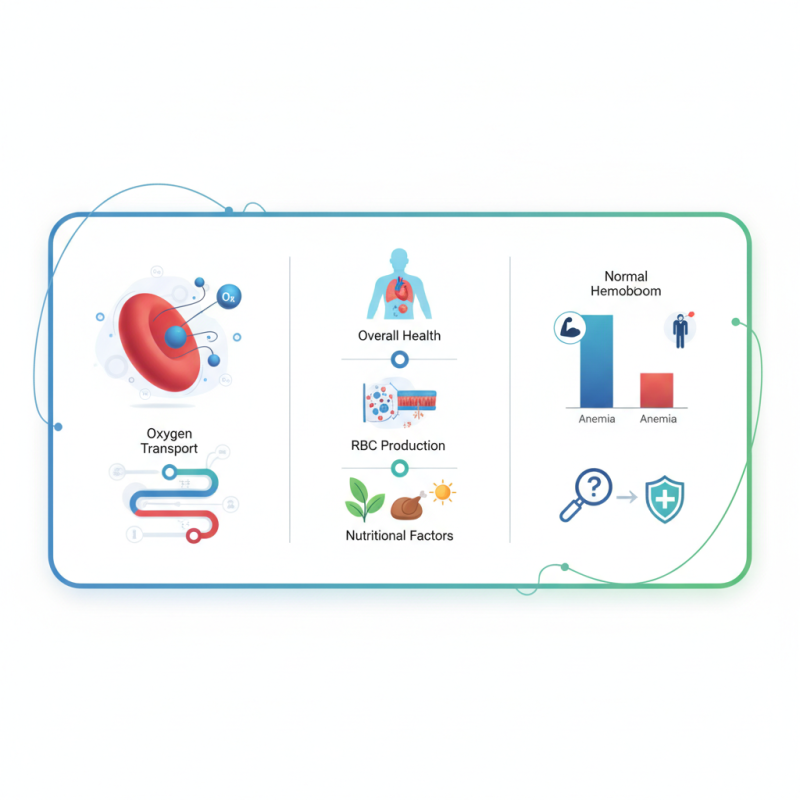
Hemoglobin is a protein found in red blood cells that plays a critical role in transporting oxygen from the lungs to the tissues and organs throughout the body. It binds with oxygen molecules, allowing our blood to deliver essential oxygen for cellular metabolism, which is crucial for maintaining overall health. Aside from oxygen transport, hemoglobin is also involved in the regulation of blood pH, supporting the acid-base balance of the body. Abnormal levels of hemoglobin can indicate various health issues, such as anemia, which affects approximately 1.62 billion people worldwide, according to the World Health Organization.
Monitoring hemoglobin levels through regular blood tests is essential for detecting potential health problems early. For instance, individuals with low hemoglobin levels may experience fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath, which can significantly impact their quality of life. On the other hand, elevated levels may indicate dehydration or other underlying conditions. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) highlights that understanding hemoglobin levels can aid in diagnosing and effectively managing diverse health conditions, making it a key component of routine medical assessments.
Tips: To maintain healthy hemoglobin levels, consider incorporating iron-rich foods such as lean meats, legumes, and leafy green vegetables into your diet. Staying hydrated is equally important, as proper hydration supports optimal blood volume and circulation. Regular exercise can also enhance oxygen circulation in the body, promoting better hemoglobin function.
A hemoglobin blood test is a crucial procedure that helps evaluate your overall health by measuring the amount of hemoglobin in your blood, which is essential for transporting oxygen throughout the body. The process is simple and typically involves a healthcare provider taking a blood sample from a vein in your arm. This sample is then sent to a lab for analysis, where the results can indicate potential conditions such as anemia, dehydration, or blood loss.
During the test, it’s important to follow some key tips to ensure accurate results. First, stay hydrated; drinking water before the test can make it easier to draw blood. Additionally, inform your healthcare provider about any medications or supplements you’re taking, as some substances can affect hemoglobin levels. Lastly, while fasting is usually not necessary for this test, it's always a good idea to check with your doctor regarding specific instructions.
After the test, you may receive your results within a few days. These results are crucial for determining your health status as they can reveal deficiencies or other medical concerns. If levels are found to be abnormal, your doctor may recommend further testing or treatment to address any underlying issues. Being proactive about understanding your hemoglobin levels can significantly contribute to maintaining optimal health.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| What is a Hemoglobin Blood Test? | A diagnostic test that measures the amount of hemoglobin in the blood. |
| Purpose | To assess the oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood, evaluate anemia, and monitor overall health. |
| Who Should Get Tested? | Individuals with symptoms of anemia, chronic diseases, or before surgery. |
| Preparation | No special preparation is needed. |
| Results Interpretation | Normal ranges: 13.8 to 17.2 grams per deciliter for men, and 12.1 to 15.1 grams per deciliter for women. |
| Common Conditions Detected | Anemia, polycythemia vera, and other blood disorders. |
| Follow-Up Actions | Discuss results with a healthcare provider for possible further testing or treatment. |
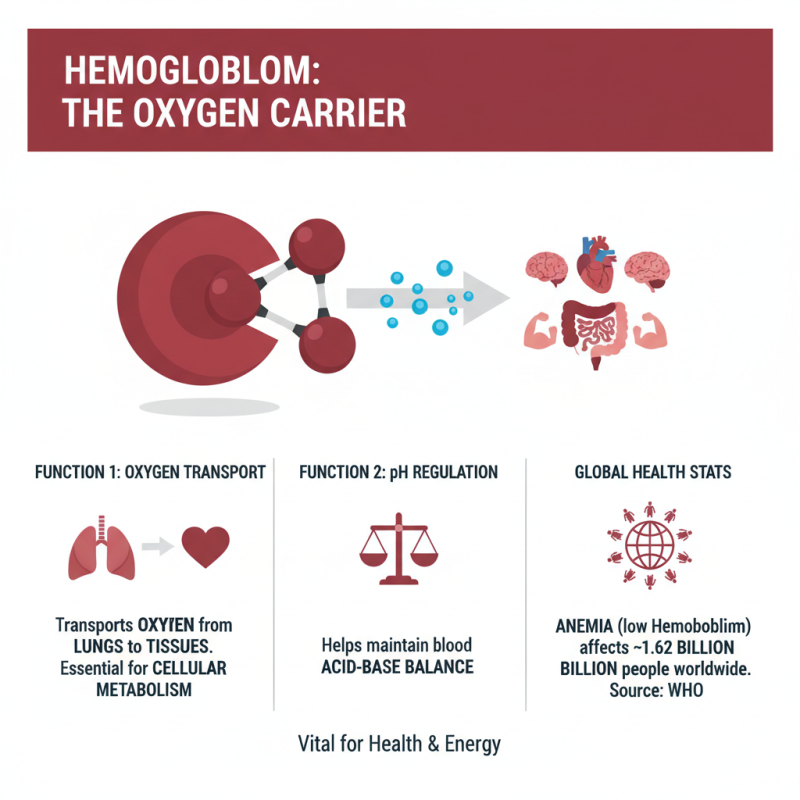
A hemoglobin blood test is a vital diagnostic tool that measures the amount of hemoglobin in your blood, an essential protein in red blood cells responsible for transporting oxygen throughout the body. Regularly monitoring hemoglobin levels can be crucial for identifying various health issues, particularly anemia. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), anemia affects approximately 1.62 billion people worldwide, highlighting the significance of this test in detecting conditions that could lead to fatigue, weakness, and other serious health concerns.
There are several key reasons to prioritize testing your hemoglobin levels. First, low hemoglobin can indicate underlying health issues such as nutritional deficiencies, chronic diseases, or bone marrow problems. For instance, data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) suggests that iron deficiency anemia is prevalent, especially among women and children, affecting about 9-12% of the U.S. population in these demographics. Monitoring hemoglobin levels can help address these deficiencies early on. Second, elevated hemoglobin levels may indicate dehydration or other medical conditions, such as heart disease or lung disease, which require further investigation. Regular testing not only aids in prompt diagnosis but also supports proactive health management, ensuring that any potential issues are addressed before they progress into more serious health complications.
Hemoglobin test results are crucial indicators of overall health. They reveal important information about the oxygen-carrying capacity of your blood and can help diagnose various medical conditions. Hemoglobin is the protein in red blood cells that binds to oxygen, and normal levels usually range from 13.8 to 17.2 grams per deciliter for men and 12.1 to 15.1 grams per deciliter for women. When interpreting these results, healthcare providers look for abnormalities such as low levels, which can indicate anemia or other underlying health issues. On the other hand, elevated hemoglobin levels may suggest dehydration or lung disease, requiring further investigation.
Understanding your hemoglobin levels empowers you to be proactive about your health. If results fall outside the normal range, your physician may recommend additional tests or dietary changes to address the underlying causes. Regular monitoring is particularly important for individuals with chronic illnesses or those who experience symptoms like fatigue or shortness of breath. Ultimately, interpreting these results within the broader context of your health history can lead to timely interventions and better management of your well-being.
Abnormal hemoglobin levels can be indicative of several common health conditions that require attention. For instance, low hemoglobin levels often point towards anemia, a condition characterized by insufficient red blood cells to carry adequate oxygen to the body's tissues. Anemia can result from various factors, including nutrient deficiencies, such as iron, vitamin B12, or folate, or chronic diseases that interfere with red blood cell production. Symptoms may include fatigue, weakness, and pale skin, prompting further investigation and treatment.
On the other hand, elevated hemoglobin levels may suggest conditions such as polycythemia vera, which is a blood disorder leading to an increased production of red blood cells. This can result in thickened blood, raising the risk of blood clots and cardiovascular issues. Additionally, high levels may be linked to chronic hypoxia—low oxygen levels in the body due to conditions such as lung disease or living at high altitudes. Recognizing these indicators through a hemoglobin blood test is crucial for diagnosing and managing these potential health risks effectively.