+86-18343147735
+86-18343147735




In recent years, the importance of joint health has gained significant attention, particularly as more individuals seek ways to maintain mobility and reduce discomfort associated with age or injury. One method that has emerged in the realm of joint health assessment is the Glucosamine Test, which provides valuable insights into an individual’s joint condition and overall musculoskeletal health. Dr. Jane Smith, a renowned rheumatologist and expert in joint health assessment, states, "The Glucosamine Test offers a non-invasive approach to understanding joint integrity and can play a crucial role in early diagnosis and management of joint-related issues."
As the demand for effective joint health evaluations rises, understanding the procedure and implications of the Glucosamine Test is essential for both healthcare professionals and patients alike. This test not only assesses the presence of glucosamine in the body but also helps gauge the effectiveness of treatments aimed at improving joint function and alleviating pain. By utilizing this test, individuals can make informed decisions on their joint health strategies, potentially enhancing their quality of life.
Furthermore, the Glucosamine Test serves as a critical tool in the broader landscape of preventive care, encouraging proactive measures before the onset of more severe joint-related conditions. With experts like Dr. Smith advocating for its significance, it is evident that the Glucosamine Test can be a pivotal component in the journey towards maintaining healthy, functional joints.

Glucosamine is a naturally occurring compound found in the body that plays a crucial role in maintaining joint health. It is primarily involved in the synthesis of glycosaminoglycans, which are essential components of cartilage. Cartilage serves as a cushion between bones in joints, helping to absorb shock and facilitate smooth movement. As we age or undergo repetitive stress on our joints, the natural production of glucosamine may decrease, potentially leading to joint pain and conditions like osteoarthritis.
Supplementation with glucosamine has gained popularity among individuals looking to support their joint function and alleviate discomfort. Research suggests that glucosamine may help slow cartilage breakdown and promote the repair of damaged joint tissue, thereby improving mobility and reducing pain. While the efficacy of glucosamine supplementation can vary among individuals, many report positive experiences in managing their joint health. Understanding the role of glucosamine can empower individuals to make informed choices about their joint health strategies, potentially leading to better outcomes in maintaining an active lifestyle.
This chart displays the impact of glucosamine supplementation on joint health scores over a period of six months. Regular assessments indicate an improvement in joint health as measured on a scale from 1 to 10, where 10 indicates optimal joint health.
Before undergoing a glucosamine test for joint health assessment, it’s essential to prepare adequately to ensure accurate results. The test typically involves evaluating the levels of glucosamine in your body, a compound that plays a crucial role in maintaining cartilage health in joints. Prior to testing, discuss with your healthcare provider any medications you are currently taking, as certain supplements or drugs can influence glucosamine levels. Typically, it is advised to refrain from taking glucosamine supplements for a few days leading up to the test.
In addition to dietary considerations, maintaining a healthy lifestyle can aid in achieving comprehensive test results. Hydration is vital; drinking plenty of water helps in the metabolism of nutrients and can impact the effectiveness of the test. It's also beneficial to avoid high-stress activities or potentially inflammatory foods, as stress and diet can alter joint health indicators. Ensuring a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods leading up to the test can provide a clearer picture of your joint health. Being mindful of these preparatory measures can contribute significantly to the test’s efficacy and reliability.
Performing a glucosamine test for joint health assessment can be a straightforward process if you follow a structured approach. Begin by gathering all necessary supplies, including glucosamine supplements, a measuring cup, a notepad for recording observations, and a timer. Start the test by taking the recommended dosage of glucosamine consistently for a specific duration, typically two to four weeks. During this period, meticulously record any changes in joint pain, mobility, or overall comfort levels. Regularly assess your joint health by noting down your levels of discomfort before and after movement or activity.
Tips: It’s important to maintain consistency in your testing routine; taking glucosamine at the same time each day can help yield clearer results. Additionally, keep an eye on your diet and exercise habits throughout the testing period, as these factors can significantly impact your joint health and may influence the outcome of your glucosamine assessment.
After completing the test duration, review your notes to evaluate any improvements or side effects. If possible, compare your results with any pre-existing joint health assessments or discuss them with a healthcare professional. They can provide additional insights into the effectiveness of glucosamine for your specific situation and recommend next steps based on your findings. Keep in mind that individual responses may vary, and it’s essential to tailor any joint health strategy to your personal needs and health status.
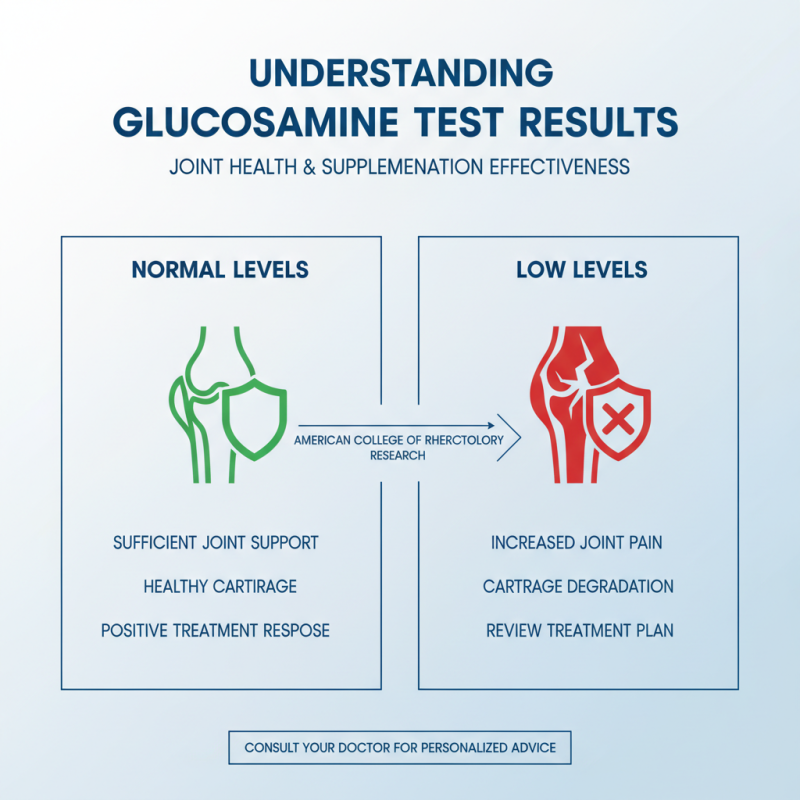
Interpreting your glucosamine test results is crucial for understanding your joint health and the effectiveness of your supplementation. Glucosamine is a naturally occurring compound found in cartilage, and its levels can indicate the health of your joints. According to research published by the American College of Rheumatology, a glucosamine test can help in assessing not only the degradation of cartilage but also how well your joints are responding to treatment. Generally, normal glucosamine levels suggest sufficient joint support, while low levels may correlate with increased joint pain and discomfort.
When you receive your results, it's essential to consider them alongside other markers of joint health. A study in the Journal of Orthopaedic Research found that individuals with glucosamine levels below the baseline often exhibited higher instances of osteoarthritis and joint inflammation. If your test shows reduced levels, your healthcare provider may suggest an adjusted intake of glucosamine or additional supplements to support cartilage regeneration. In contrast, elevated levels can indicate a healthy response, but if accompanied by pain or dysfunction, further investigation into other underlying conditions may be warranted. Engaging with a healthcare professional can provide deeper insights into your specific results and help tailor a comprehensive joint health management plan.

After conducting a glucosamine test for joint health, it’s essential to take appropriate follow-up actions to ensure that you are addressing any issues that may have been identified. Depending on the results of the test, you might need to consult a healthcare professional, particularly if there are indications of joint damage or deterioration. They can provide a tailored treatment plan that fits your specific conditions, including lifestyle adjustments, dietary recommendations, or physical therapies focused on improving joint function.
Tips for Effective Follow-Up Actions: It's vital to keep a record of your symptoms and any changes you experience after the test. Journaling can help you communicate effectively with your healthcare provider. Additionally, consider engaging in regular low-impact exercises, such as swimming or cycling, to strengthen your joints without causing further stress. Moreover, maintaining a balanced diet enriched with anti-inflammatory foods can support your joint health long-term.
Furthermore, staying informed about joint health can empower you in your recovery process. Researching about the roles of various supplements and dietary choices in joint care can make a significant difference. Joining support groups or online communities can also provide encouragement and advice from others on the same journey, helping you maintain motivation and achieve better overall joint health.