+86-18343147735
+86-18343147735




A blood test is a critical medical procedure that plays a vital role in diagnosing various health conditions and monitoring overall wellness. Through the analysis of blood samples, healthcare professionals can gain valuable insights into a patient's physical state, detect diseases, and evaluate organ function. The importance of blood tests cannot be overstated, as they serve as a window into the body's inner workings, providing essential data that guides treatment decisions and health recommendations.
There are various types of blood tests, each designed to assess specific aspects of health. Common tests include complete blood counts (CBC), which measure different components of blood, and metabolic panels that evaluate chemical balance and metabolism. Understanding these tests and their implications is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers alike. As advancements in medical technology continue to evolve, the landscape of blood testing is expanding, enhancing our ability to detect and manage health issues more effectively.
In summary, the significance of blood test blood analysis in the realm of medical diagnostics is indisputable. By further exploring the types and applications of these tests, individuals can better appreciate their role in health maintenance and disease prevention.


A blood test is a fundamental medical procedure that involves the analysis of blood samples to assess an individual's health status. This diagnostic tool is invaluable for detecting various conditions, monitoring chronic diseases, and determining overall organ function. According to the latest report by the World Health Organization, approximately 1.4 billion blood tests are conducted annually worldwide, underscoring the critical role they play in modern medicine.
The process of a blood test typically begins with a healthcare professional collecting a small sample of blood, often from a vein in the arm. This sample is then sent to a laboratory where it undergoes various analyses, including complete blood counts, biochemical panels, and specialized tests. Each type of blood test serves a unique purpose; for example, a complete blood count (CBC) can reveal signs of anemia, infection, or other hematological disorders, while a metabolic panel provides insights into organ function and nutritional status. Data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention indicate that timely blood testing contributes significantly to early disease detection and improved patient outcomes, highlighting the necessity and benefits of regular health screenings.
Blood tests are critical diagnostic tools used in modern medicine, providing essential insights into an individual's health. There are various types of blood tests, each serving a specific purpose. Complete Blood Count (CBC) tests measure components like red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets, allowing clinicians to diagnose conditions such as anemia, infections, and various blood disorders. According to a 2021 report by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), approximately 50% of patients receiving preventive care annually undergo at least one CBC, highlighting its importance in routine health assessments.
Another essential category is the metabolic panel, which evaluates the body’s chemical balance and metabolism. This panel typically includes tests for glucose, calcium, electrolytes, and kidney and liver enzymes. The American Association for Clinical Chemistry reports that these tests help in monitoring chronic conditions like diabetes and kidney disease, with around 70% of chronic disease management decisions relying on biochemical tests, including metabolic panels. Furthermore, lipid panels, which assess cholesterol levels, are crucial for cardiovascular health. The National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute indicates that about one in three adults has high cholesterol levels, reinforcing the need for regular testing to prevent heart disease. These diverse blood tests collectively play a vital role in preventative health care and ongoing disease management, underscoring their significance in clinical practice.
| Type of Blood Test | Purpose | What it Measures |
|---|---|---|
| Complete Blood Count (CBC) | Assess overall health and detect a variety of disorders | Red blood cells, white blood cells, hemoglobin, platelets |
| Basic Metabolic Panel (BMP) | Evaluate kidney function and electrolyte levels | Glucose, calcium, electrolytes (sodium, potassium, bicarbonate, chloride) |
| Lipid Panel | Assess risk of heart disease | Cholesterol levels (total cholesterol, LDL, HDL, triglycerides) |
| Liver Function Tests | Evaluate the health of the liver | Enzymes, bilirubin, proteins (albumin) |
| Thyroid Function Tests | Assess thyroid health and function | Thyroid hormones (TSH, T3, T4) |
A blood test is a crucial diagnostic tool that helps healthcare professionals assess an individual's health status, detect diseases, and monitor various health conditions. Understanding the process of a blood test can demystify what often seems intimidating. Typically, the procedure begins with a healthcare provider selecting the appropriate type of blood test based on the patient’s symptoms and medical history. This involves drawing blood, which is usually obtained from a vein in the arm using a sterile needle. The collected blood is then sent to a laboratory where it undergoes various analyses.
Throughout this process, it's important to remember a few tips for a smoother experience. Ensure you are well-hydrated before your test, as this can make veins more prominent and easier to access. Additionally, inform your healthcare provider about any medications or supplements you are taking, as these can affect test results. Lastly, relax your arm during the blood draw; tension can make it more difficult for the technician and may increase discomfort.
Once the blood samples are analyzed, the results are shared with the patient and discussed with a healthcare provider to explain their implications. Understanding this process can alleviate anxiety and encourage proactive health management. Taking note of preparation guidelines, such as fasting or dietary restrictions, is also vital for obtaining accurate test results.
The bar chart above illustrates the number of various blood tests conducted annually. Understanding these tests helps in assessing health conditions, diagnosing diseases, and monitoring treatment plans.
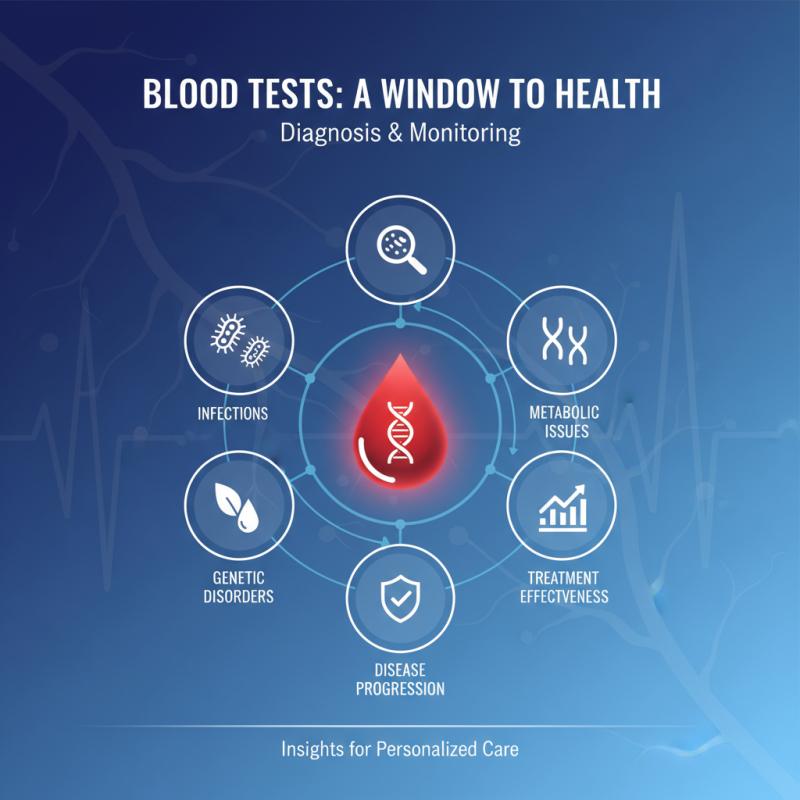
Blood tests play a crucial role in the diagnosis and monitoring of various diseases, acting as a window into a patient's overall health. By analyzing blood samples, healthcare professionals can gain insights into a wide range of conditions, including infections, genetic disorders, and metabolic issues. The tests can reveal the presence of specific markers that indicate the progression of diseases or the effectiveness of treatments, allowing for timely interventions and adjustments to care plans.
Moreover, regular blood tests can serve as preventive measures, identifying potential health risks before they become more serious. For example, routine lipid panels can help assess cholesterol levels and the risk of cardiovascular diseases, while complete blood counts can detect abnormalities in red and white blood cells that may signal underlying health issues. In this way, blood testing not only assists in making accurate diagnoses but also empowers patients with knowledge about their health, encouraging proactive management and lifestyle adjustments where necessary.
Interpreting blood test results is crucial for understanding an individual's health status. Each test provides a range of values that help healthcare providers make informed decisions. For instance, a complete blood count (CBC) measures components like red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets, which are essential for diagnosing conditions such as anemia or infections. According to the American Association for Clinical Chemistry, typical values for red blood cell count in men are approximately 4.7 to 6.1 million cells per microliter, while in women, the standard range is around 4.2 to 5.4 million cells per microliter. Deviations from these ranges can signal underlying health issues that may require further investigation.
Additionally, metabolic panels assess various chemical components in the blood, providing insight into the body’s metabolic state. Common markers like glucose, calcium, and electrolytes are analyzed to evaluate kidney function and heart health. The National Institutes of Health reports that abnormal glucose levels can indicate diabetes, with normal fasting blood sugar levels falling between 70 to 99 mg/dL. Understanding these values is vital for patients and healthcare providers alike, as they guide treatment plans and lifestyle changes necessary for maintaining optimal health. Proper interpretation of these blood test results empowers individuals to take charge of their health and fosters a proactive approach to wellness.