+86-18343147735
+86-18343147735




As diabetes prevalence continues to rise, effective management strategies are essential. According to the International Diabetes Federation, approximately 537 million adults are living with diabetes globally. This alarming statistic highlights the critical need for advanced Glucose Testing methods. The right testing tools empower patients to monitor their blood sugar levels accurately, minimizing complications.
Dr. Sarah Mitchell, a leading expert in diabetes care, emphasizes the importance of reliable glucose monitoring. She states, "Accurate Glucose Testing is a cornerstone of diabetes management.” This perspective underlines the vital role that innovative testing technologies play in enhancing patient outcomes. Current methods vary widely in terms of accuracy, user-friendliness, and availability.
With new technologies emerging, the landscape of Glucose Testing is evolving. Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) systems have gained traction, yet traditional fingerstick tests remain in use. Patients often face challenges in adhering to their testing regimens. Understanding these methods is crucial for effective diabetes management. Thus, evaluating the best practices for Glucose Testing is more important than ever.
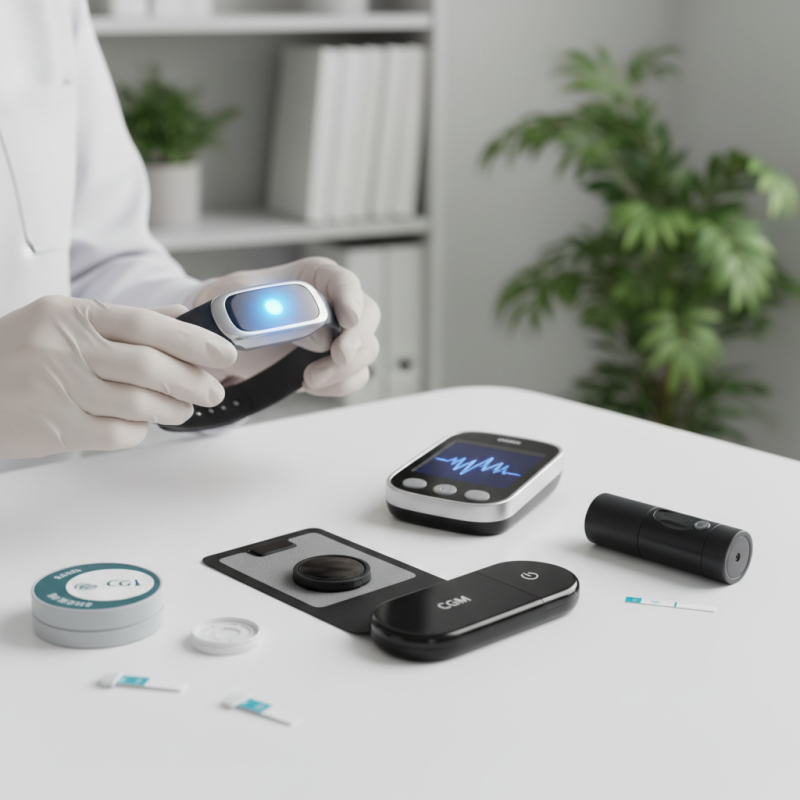

Innovative glucose testing technologies are transforming diabetes management. Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) are at the forefront of this revolution. These devices provide real-time glucose readings, allowing users to track their levels more effectively. Patients no longer need to rely solely on periodic finger sticks. Instead, they enjoy a more ongoing understanding of how different foods and activities affect their glucose levels.
Another emerging technology is the use of smart insulin pens. These devices can connect to smartphones, offering personalized insights and dosage recommendations. Some users may find this integration helpful, but it can sometimes feel overwhelming. The learning curve can be steep, and not everyone adapts easily. Additionally, there are concerns about data privacy with such connected devices. Balancing convenience and security remains a challenge.
Wearable glucose monitoring patches are also gaining traction. These patches enable non-invasive testing, making it easier for users to monitor their glucose without discomfort. However, some users express skepticism about their accuracy. They argue that these methods need refinement. The future of diabetes management relies heavily on technology. Yet, it is essential for users to remain critical and informed while navigating these advances.
Blood glucose meters have been essential tools for diabetes management. These devices measure glucose levels in the blood, providing crucial data for individuals managing diabetes. However, traditional meters have limitations. They often require a blood sample from a finger prick, which can be painful and inconvenient, especially for frequent testing.
Accuracy is vital in blood glucose readings, yet some traditional meters may produce inconsistent results. Factors like temperature and humidity can affect readings. Additionally, users often struggle to interpret results effectively. Over time, men and women alike can become frustrated with these devices. Regular calibration is necessary, yet many forget this step. This lapse can lead to misguided treatment decisions.
Understanding the method of testing is as important as the results themselves. While traditional blood glucose meters remain widely used, they have sparked discussions about advancement. Many patients wonder if emerging technologies might offer improved accuracy and comfort. Continuous glucose monitors, for example, eliminate the need for finger pricks altogether. Such options highlight the need for ongoing reflection on traditional methods. This is an evolving landscape, and users should remain open to new possibilities.
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) systems are revolutionizing diabetes management. Unlike traditional blood glucose meters, CGMs provide real-time glucose levels. This technology can alert users to high or low glucose levels, enabling timely action. According to recent studies, CGMs have been linked to a 0.5% reduction in HbA1c levels. This data suggests they play a significant role in improving long-term glucose control.
Features of CGMs include ease of use and integration with smartphones. Users can track their levels on their devices, making management more accessible. However, not all CGMs are created equal. Some users experience discomfort with sensor insertion. Moreover, sensor accuracy can vary, leading to occasional false readings. A report from the Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology indicated that around 20% of users reported frustration with sensor reliability.
Benefits of CGMs extend beyond meters. They encourage lifestyle adjustments. Users can see the impact of food on glucose levels immediately. However, CGMs can become overwhelming. Data overload may lead to anxiety for some individuals. This highlights the need for proper education and support in using CGMs effectively. For many, the balance between technology and personal management remains a work in progress.
| Method | Features | Benefits | User Experience |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fingerstick Testing | Quick results, portable | Affordable, widely available | Simple to use but may cause discomfort |
| Continuous Glucose Monitoring | Real-time glucose readings, alerts | Improved glucose control, reduced A1C levels | Convenient, less fingersticks |
| Flash Glucose Monitoring | Scannable sensor, painless | Immediate access to glucose data | User-friendly; enhances lifestyle |
| Smartphone apps with Blood Glucose Meter | Data sync, trends analysis | Integrates lifestyle tracking | Engaging; encourages adherence |
| Urine Glucose Testing | Non-invasive, simple | Cost-effective | Not as accurate; best for screening |

Recent advancements in non-invasive glucose testing methods are garnering significant attention. Traditional methods often involve painful finger pricks and regular blood draws. Many people find this inconvenient and uncomfortable. In contrast, non-invasive techniques aim to measure glucose levels without skin penetration. This shift could change the lives of those managing diabetes.
Current research explores various methods, including optical sensors and electromagnetic techniques. For instance, some devices use near-infrared light to detect glucose levels through the skin. This technology is still evolving, and researchers are continuously refining accuracy. Other methods involve using electrical sensors to measure glucose through sweat or interstitial fluid. However, these technologies may not yet provide reliable results for everyone.
The future of non-invasive glucose monitoring holds promise, but challenges remain. User acceptance is one concern, as seen with early devices. Cost and accessibility are also important factors to address. Continued research is needed to enhance accuracy and usability. Ensuring these methods fit seamlessly into daily life can be a game-changer for diabetes management.
Mobile apps and wearable devices are transforming diabetes management. These tools provide users with real-time data on blood glucose levels. Many apps allow users to log meals and activities, making it easier to identify patterns. Some wearables measure glucose through interstitial fluid. This can reduce the need for finger pricks. However, not all devices are equally accurate.
Users often report that not every app is user-friendly. Some have complicated interfaces. It can be frustrating to navigate through them, leading to disengagement. Moreover, data security is a concern. Sensitive health information needs protection, and not all apps prioritize this.
Devices can also create a false sense of security. Relying solely on technology might lead to overlooking traditional health practices. Users may forget to listen to their bodies. Collaboration with healthcare professionals remains crucial. Technology cannot replace personal medical advice, but it can enhance the overall management plan.